What is Neuropathy?
Neuropathy means nerve disease or damage.
Peripheral neuropathy is a condition that develops because of damage to the peripheral nervous system - the vast communications network that transmits information between the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) and every other part of the body.
Peripheral nerves send sensory information back to the brain and spinal cord, such as a message that the feet are cold. Peripheral nerves also carry signals from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles to generate movement. Damage to the peripheral nervous system interferes with these vital connections. Peripheral neuropathy distorts and sometimes interrupts messages between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body.
Peripheral neuropathy is the most common form of neuropathy caused by diabetes. Nerve damage occurs in an ascending pattern. The first nerve fibers to malfunction are the ones that travel the furthest from the brain and the spinal cord. Because the nerves leading to your feet are so long, it’s most often these nerves that are damaged; there’s more of them to be damaged. This nerve damage can lead to the foot problems often associated with diabetes, including foot deformities, infections, ulcers, and amputations.
Diabetes frequently leads to impaired blood flow to nerves. Pain and numbness often are felt symmetrically in both feet followed by a gradual progression up both legs. Later, the fingers, hands, and arms may become affected.
Peripheral Nerve Damage Symptoms
Symptoms are dependent on which nerves have been damaged. In general, peripheral neuropathy symptoms develop gradually; they may seem like minor and infrequent pains or problems at first, but as the nerves become more damaged, symptoms may grow.
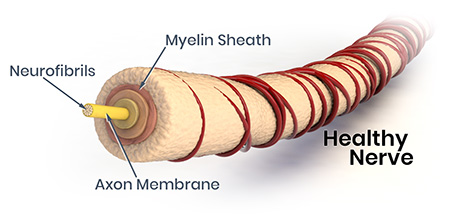
Sensory nerve damage causes a variety of symptoms because sensory nerves have a broad range of functions. Larger sensory fibers enclosed in myelin register vibration, light touch, and position sense. Damage to large sensory fibers impairs touch, resulting in a general decrease in sensation. Since this is felt most in the hands and feet, people may feel as if they are wearing gloves and stockings even when they are not. This damage to larger sensory fibers may contribute to the loss of reflexes. Loss of position sense often makes people unable to coordinate complex movements like walking or fastening buttons, or to maintain their balance when their eyes are shut.
Smaller sensory fibers without myelin sheaths transmit pain and temperature sensations. Damage to these fibers can interfere with the ability to feel pain or changes in temperature. People may fail to sense that they have been injured from a cut or that a wound is becoming infected. Others may not detect pain that warns of impending heart attack or other acute conditions. Loss of pain sensation is a particularly serious problem for people with diabetes, contributing to the high rate of lower limb amputations among this population.
Neuropathic pain is a common, often difficult to control symptom of sensory nerve damage and can seriously affect emotional well-being and overall quality of life. Often worse at night, neuropathic pain seriously disrupts sleep and adds to the emotional burden of sensory nerve damage. Neuropathic pain can often be associated with an over sensitization of pain receptors in the skin, so that people feel severe pain (allodynia) from stimuli that are normally painless. For example, some may experience pain from bed sheets draped lightly over the body. Over many years, sensory neuropathy may lead to changes in the skin, hair, as well as to joint and bone damage. Unrecognized injuries due to poor sensation contribute to these changes, so it is important for people with neuropathy to inspect numb areas for injury or damage.*



